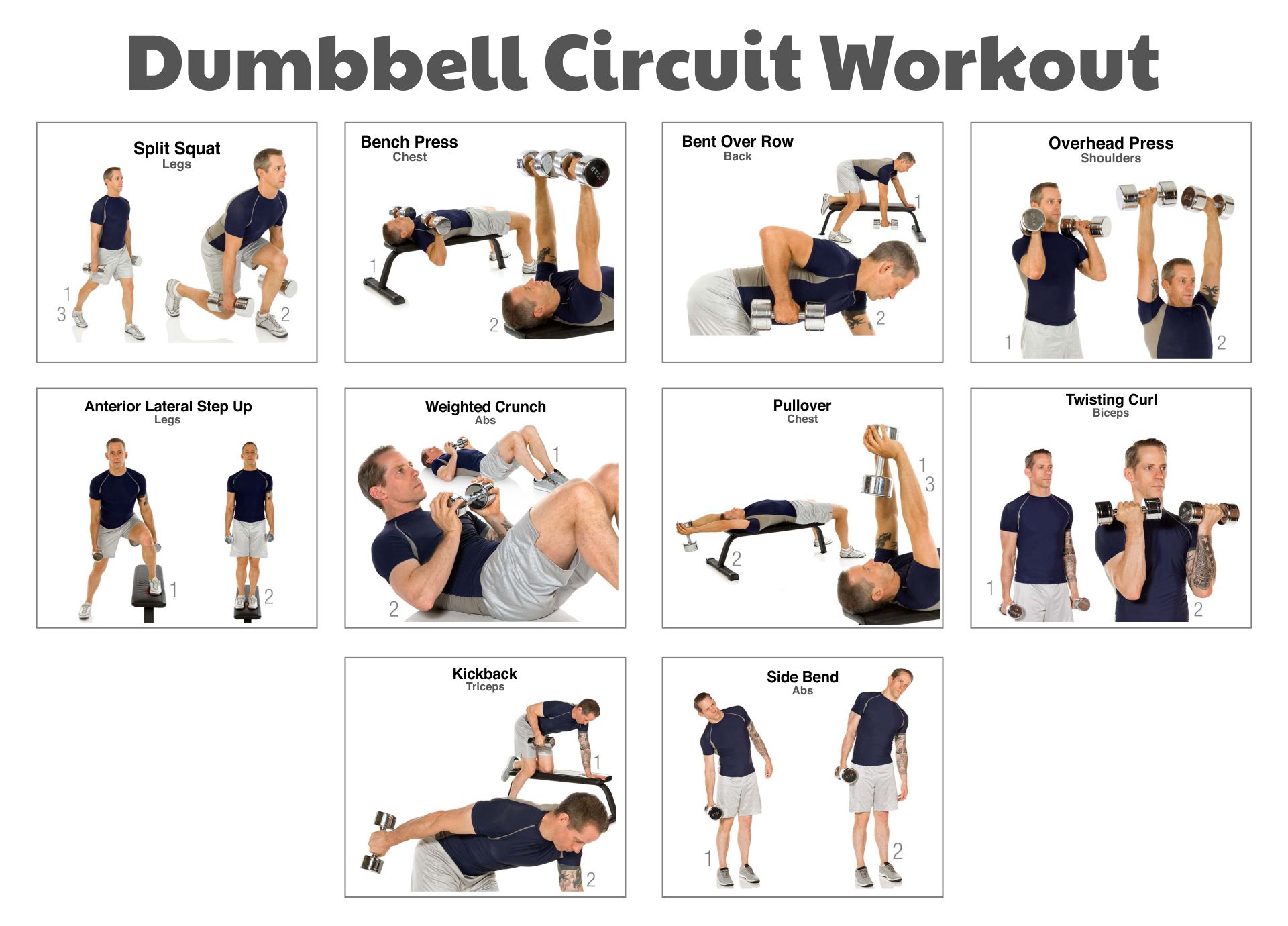
Good weight lifting workouts are more than just lifting heavy; they’re a journey towards enhanced strength, improved physique, and overall well-being. This guide delves into the fundamentals of effective weight training, providing structured programs for various fitness levels, from beginner to advanced. We’ll explore proper form, essential exercises, nutritional considerations, and injury prevention strategies to ensure a safe and rewarding experience. Understanding the nuances of different training styles, such as powerlifting, bodybuilding, and Olympic weightlifting, will empower you to tailor your workouts to your specific goals.
We will cover a range of topics including designing personalized workout plans, mastering proper lifting techniques for exercises like the bench press, squat, and deadlift, and understanding the crucial role of nutrition and recovery in achieving optimal results. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to embark on a successful and sustainable weightlifting journey.
Introduction to Effective Weight Lifting
Weightlifting offers a multitude of benefits extending far beyond simply building muscle. It’s a highly effective method for improving overall health and fitness, contributing to increased strength, bone density, metabolism, and even mental well-being. Regular weight training can lead to significant improvements in cardiovascular health, reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, it promotes a positive body composition, helping individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Proper form and technique are paramount in weightlifting. Neglecting these fundamentals significantly increases the risk of injuries, ranging from minor muscle strains to serious joint damage. Maintaining correct posture, utilizing a full range of motion, and controlling the weight throughout each repetition are crucial for maximizing effectiveness and minimizing the risk of injury. Learning proper form from a qualified instructor or through reputable resources is an essential investment in long-term success and safety.
Different Weightlifting Training Styles
Weightlifting encompasses a variety of training styles, each with its unique goals and methodologies. Powerlifting focuses on maximizing strength in three core lifts: the squat, bench press, and deadlift. Bodybuilding emphasizes building muscle mass and achieving a specific aesthetic physique through a combination of weight training, nutrition, and sometimes, supplementation. Olympic weightlifting, on the other hand, involves two dynamic lifts: the snatch and the clean and jerk, demanding explosive power and technical proficiency. The choice of training style depends largely on individual goals and preferences. For instance, an athlete preparing for a powerlifting competition would prioritize powerlifting techniques, while someone focused on improving overall physique might adopt a bodybuilding approach. The distinct demands of each style necessitate tailored training programs and attention to specific muscle groups and movement patterns.
Proper Lifting Techniques and Form
Mastering proper lifting techniques is paramount for maximizing results and minimizing the risk of injury in weightlifting. Correct form ensures that the targeted muscles are effectively engaged, while simultaneously protecting your joints and connective tissues from undue stress. This section will detail proper form for key compound lifts, common mistakes, and the importance of warm-up and cool-down routines.
Bench Press Technique
The bench press, a cornerstone of upper body strength training, involves lying supine on a bench, grasping a barbell with an overhand grip slightly wider than shoulder-width, and lowering the bar to the chest before pressing it back up. Proper form includes maintaining a stable, flat back, keeping feet flat on the floor, and engaging the core muscles throughout the movement. The bar should descend to the lower chest, making contact gently, and be controlled throughout both the lowering and lifting phases. Avoid bouncing the bar off your chest. A controlled movement minimizes the risk of injury and maximizes muscle activation.
Squat Technique
The squat, a fundamental compound exercise, targets the legs and glutes. Begin by standing with feet shoulder-width apart, toes slightly outward. Maintain an upright torso, engaging your core, and lower your hips as if sitting back into a chair. Keep your weight balanced on your heels, avoiding letting your knees cave inwards. The depth of the squat should be to where your hips are lower than your knees, but avoid excessive rounding of the lower back. The ascent should be a controlled and powerful movement driven by your legs and glutes.
Deadlift Technique
The deadlift, another fundamental compound exercise, involves lifting a weighted barbell from the floor to a standing position. Begin by standing with your feet hip-width apart, centered over the barbell. Bend at the hips and knees, maintaining a straight back and grabbing the bar with an overhand grip slightly wider than shoulder-width. Engage your core muscles and, keeping your back straight, lift the bar by extending your hips and knees simultaneously. Maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement. Avoid rounding your back, which puts excessive stress on the spine. Lower the weight under control, reversing the movement.
Common Weightlifting Mistakes and Corrections
Several common mistakes can significantly impact the effectiveness and safety of weightlifting. These mistakes often stem from improper form or neglecting essential pre- and post-workout routines.
Warm-up and Cool-down Routines
A proper warm-up prepares your body for the stresses of weightlifting, increasing blood flow to muscles and improving joint mobility. A dynamic warm-up, involving movements like arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists, is recommended. A cool-down, consisting of light cardio and stretching, helps reduce muscle soreness and improve recovery. Failing to adequately warm-up increases the risk of injury, while neglecting a cool-down can hinder recovery and increase muscle soreness.
End of Discussion
Embarking on a weightlifting journey requires dedication, consistency, and a solid understanding of the principles involved. This guide has provided a framework for building effective and safe weightlifting routines, emphasizing proper form, progressive overload, and the importance of nutrition and recovery. Remember to listen to your body, prioritize safety, and adapt your training to your individual needs and progress. With consistent effort and a commitment to these principles, you can achieve significant gains in strength, muscle mass, and overall fitness. The rewards extend beyond the physical, fostering discipline, resilience, and a sense of accomplishment that permeates all aspects of life.